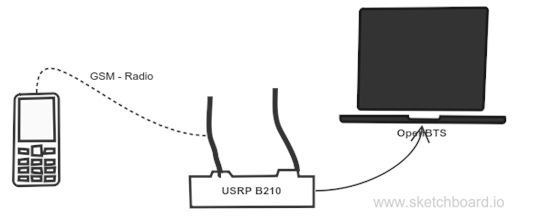
Definition of Cyber War – A nation state conducting sabotage and espionage against another nation in order to cause disruption or to extract data. This could involve the use of Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs).
Definition of Cyberspace – The notional environment in which communication over computer networks occurs.
Ransomware – A type of malware which restricts access to the computer system that it infects. Ransomware encrypts data on your PC so you can’t access or use your files. Normally many Ransomware attacks won’t unencrypt your data until you pay a large fee to do so.
Cyber espionage – Is becoming the weapon of choice for many national governments – no matter how tight-lipped they may be about any involvement in such activities to undermine their enemies. As Nesbitt said, “the next world war will be fought on a keyboard,” We should expect cyber espionage attacks to increase in frequency in 2016.
Cyber Theft – The stealing of financial information is nothing new. With stolen credit or debit card data on the black market, this makes for a well-established and lucrative business for cyber criminals.
Insecure Passwords – Easy to crack passwords will continue to be a big risk and is likely to be the first year when the password starts to be phased out in favour of a number of different multi-factor options. Next year may well be the first year of multi-factor by default,”Digital Shadows”, a cyber threat intelligence company said.
Internet of things – The ‘Internet of Things’ is a term that describes a world in which physical devices like home appliances and cars are connected to the Internet and can be synced so users can control everything from a single app. The Internet of Things will be integrated into every market you can think of and especially the marine industry network to save money and time, but it hasn’t been designed with security in mind. There are millions of hackers out there that could compromise these interconnected systems. We have sacrificed security for efficiency.